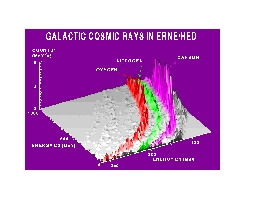
Galactic cosmic radiation consists of particles originating in the Milky Way, including atomic nuclei heavier than helium possibly coming from supernovas. Due to transport effects, the galactic cosmic rays are characterised by their rising spectrum. Of this radiation, the ERNE HED (High Energy Detector) has succeeded in identifying larger amounts of at least hydrogen, helium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon and iron. An example of composition and energy resolution is shown in the picture below (fig. 2). The two horizontal axes describe energy deposited by the incoming particle in two detector layers. The vertical axis has the observed count rate. Carbon (the highest peak), nitrogen and oxygen are seen in this picture. To the right of the carbon ridge, some boron can be found, as well as some neon to the left of oxygen.
Downloads
- Full-size image [JPG, 140K]
- Medium-size image [JPG, 24K]
- Hi-resolution size image [TIF, 476K]
- Medium-size image [JPG, 24K]